For many years, people with terminal illnesses were an embarrassment for doctors. Someone who could not be cured was evidence of the doctors’ fallibility, 
and as a result the doctors regularly shunned the dying with the excuse that there was nothing more that could be done (and that there was plenty of other demand on the doctors’ time).
Elizabeth Kübler-Ross was a doctor in Switzerland who railed against this unkindness and spent a lot of time with dying people, both comforting and studying them. She wrote a book, called ‘On Death and Dying’ which included a cycle of emotional states that is often referred to (but not exclusively called) the Grief Cycle.
In the ensuing years, it was noticed that this emotional cycle was not exclusive just to the terminally ill, but also other people who were affected by bad news, such as losing their jobs or otherwise being negatively affected by change. The important factor is not that the change is good or bad, but that they perceive it as a significantly negative event.
The Extended Grief Cycle
The Extended Grief Cycle can be shown as in the chart below, indicating the roller-coaster ride of activity and passivity as the person wriggles and turns in their desperate efforts to avoid the change.
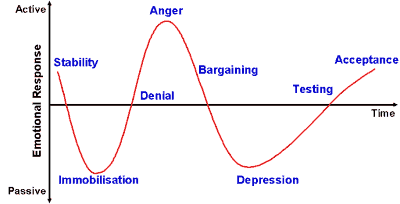
The initial state before the cycle is received is stable, at least in terms of the subsequent reaction on hearing the bad news. Compared with the ups and downs to come, even if there is some variation, this is indeed a stable state.
And then, into the calm of this relative paradise, a bombshell bursts…
-
Shock stage*: Initial paralysis at hearing the bad news.
-
Denial stage: Trying to avoid the inevitable.
-
Anger stage: Frustrated outpouring of bottled-up emotion.
-
Bargaining stage: Seeking in vain for a way out.
-
Depression stage: Final realization of the inevitable.
-
Testing stage*: Seeking realistic solutions.
-
Acceptance stage: Finally finding the way forward.
* This model is extended slightly from the original Kubler-Ross model, which does not explicitly include the Shock and Testing stages. These stages however are often useful to understand and facilitating change.
Sticking and cycling
Getting stuck
A common problem with the above cycle is that people get stuck in one phase. Thus a person may become stuck in denial, never moving on from the position of not accepting the inevitable future. When it happens, they still keep on denying it, such as the person who has lost their job still going into the city only to sit on a park bench all day.
Getting stuck in denial is common in ‘cool’ cultures (such as in Britain, particularly Southern England) where expressing anger is not acceptable. The person may feel that anger, but may then repress it, bottling it up inside.
Likewise, a person may be stuck in permanent anger (which is itself a form of flight from reality) or repeated bargaining. It is more difficult to get stuck in active states than in passivity, and getting stuck in depression is perhaps a more common ailment.
Going in cycles
Another trap is that when a person moves on to the next phase, they have not completed an earlier phase and so move backwards in cyclic loops that repeat previous emotion and actions. Thus, for example, a person that finds bargaining not to be working, may go back into anger or denial.
Cycling is itself a form of avoidance of the inevitable, and going backwards in time may seem to be a way of extending the time before the perceived bad thing happens.
See also
The positive change cycle, Coping Mechanisms, The need for control, Psychoanalysis and mourning
Elisabeth Kübler-Ross, On Death and Dying, Macmillan, NY, 1969









































