Improvement is always possible. This conviction is the heart of the transformation system developed by family therapist Virginia Satir.
Her system helps people improve their lives by transforming the way they see and express themselves. An element of the Satir System is a five-stage change model (see Figure 1) that describes the effects each stage has on feelings, thinking, performance, and physiology. Using the principles embodied in this model, you can improve how you process change and how you help others process change.
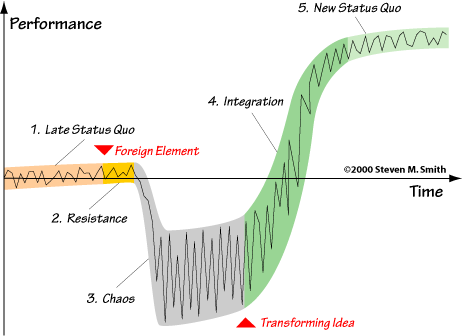
| Firgure 1. The impact on group performance of a well assimilated change during the five stages of the Satir Change Model. |
Stage 1: Late Status Quo
The group is at a familiar place. The performance pattern is consistent. Stable relationships give members a sense of belonging and identity. Members know what to expect, how to react, and how to behave.
Implicit and explicit rules underlie behavior. Members attach survival value to the rules, even if they are harmful. For instance, the chief of an engineering group has an explicit rule — all projects must be completed on schedule. When the flu halts the work of several engineers, the chief requires the group to compensate by working ten hours a day, seven days a week. After experiencing too many crises at both work and home, the engineers begin to bicker and the project falls apart.
For this group, the chief’s explicit rule about deadlines is their Late Status Quo. They don’t necessarily enjoy the amount of work they had to do, but they know and understand what is expected of them. The team feels the pressure from the chief’s rule about deadlines and compensates accordingly. The pressure works for small problems. With a major problem, like the flu, the group cannot cope with the chief’s expectations and a pattern of dysfunctional behavior starts.
Poor communication is a symptom of a dysfunctional group. Members use blaming, placating, and otherincongruent communication styles to cope with feelings like anger and guilt. Stress may lead to physical symptoms such as headaches and gastrointestinal pain that create an unexplainable increase in absenteeism.
Caught in a web of dysfunctional concepts, the members whose opinions count the most are unaware of the imbalance between the group and its environment. New information and concepts from outside the group can open members up to the possibility of improvement.
Stage 2: Resistance
The group confronts a foreign element that requires a response. Often imported by a small minority seeking change, this element brings the members whose opinions count the most face to face with a crucial issue.
A foreign element threatens the stability of familiar power structures. Most members resist by denying its validity, avoiding the issue, or blaming someone for causing the problem. These blocking tactics are accompanied by unconscious physical responses, such as shallow breathing and closed posture.
Resistance clogs awareness and conceals the desires highlighted by the foreign element. For example, a powerful minority within the marketing department of a tool manufacturer engages a consultant to do a market survey. She finds a disturbing trend: A growing number of clients believe that a competitor is producing superior quality products at a lower price. Middle and upper management vehemently deny the findings and dispute the validity of the survey methods. But after a series of frank discussions with key clients, upper management accepts the findings. They develop a vision for propelling the company into a position as the industry leader in product quality and support.
Members in this stage need help opening up, becoming aware, and overcoming the reaction to deny, avoid or blame.
Stage 3: Chaos
The group enters the unknown. Relationships shatter: Old expectations may no longer be valid; old reactions may cease to be effective; and old behaviors may not be possible.
The loss of belonging and identity triggers anxiousness and vulnerability. On occasion, these feelings may set off nervous disorders such as shaking, dizziness, tics, and rashes. Members may behave uncharacteristically as they revert to childhood survival rules. For instance, a manufacturing company cancels the development of a major new product, reduces the number of employees, and reorganizes. Many of the surviving employees lose their ability to concentrate for much of the day. Desperately seeking new relationships that offer hope, the employees search for different jobs. Both manufacturing yield and product quality takes a nosedive.
Managers of groups experiencing chaos should plan for group performance to plummet during this stage. Until the members accept the foreign element, members form only halfhearted relationships with each other. Chaos is the period of erratic performance that mirrors the search for a beneficial relationship to the foreign element.
All members in this stage need help focusing on their feelings, acknowledging their fear, and using their support systems. Management needs special help avoiding any attempt to short circuit this stage with magical solutions. The chaos stage is vital to the transformation process.
Stage 4: Integration
The members discover a transforming idea that shows how the foreign element can benefit them. The group becomes excited. New relationships emerge that offer the opportunity for identity and belonging. With practice, performance improves rapidly.
For instance, an experienced accounting group must convert to a new computer system. The group resists the new system fearing it will turn them into novices. But the members eventually discover that skill with this widely used system increases their value in the marketplace. Believing that the change may lead to salary increases or better jobs, the members begin a vigorous conversion to the new system.
Awareness of new possibilities enables authorship of new rules that build functional reactions, expectations, and behaviors. Members may feel euphoric and invincible, as the transforming idea may be so powerful that it becomes a panacea.
Members in this stage need more support than might be first thought. They can become frustrated when things fail to work perfectly the first time. Although members feel good, they are also afraid that any transformation might mysteriously evaporate disconnecting them from their new relationships and plunging them back into chaos. The members need reassurance and help finding new methods for coping with difficulties.
Stage 5: New Status Quo
If the change is well conceived and assimilated, the group and its environment are in better accord and performance stabilizes at a higher level than in the Late Status Quo.
A healthy group is calm and alert. Members are centered with more erect posture and deeper breathing. They feel free to observe and communicate what is really happening. A sense of accomplishment and possibility permeates the atmosphere.
In this stage, the members continue to need to feel safe so they can practice. Everyone, manager and members, needs to encourage each other to continue exploring the imbalances between the group and its environment so that there is less resistance to change.
I’ve observed groups, after many change cycles, become learning organizations?they learn how to cope with change. The members of these organizations are not threatened or anxious about the types of situations that they used to experience as foreign element. Instead, these situations excite and motivate them.
For example, the customer services group of a computer manufacturer learns to adapt their repair policies and techniques to any new product. Supporting a new computer system used to scare the group but not anymore. Management communicates and reinforces the vision of seamless new product support. Some members influence the design of support features for the new products. Other members plan and teach training courses. All members provide feedback to improve the process.
Postscript: Coping With Change
Virginia Satir’s Change Model describes the change patterns she saw during therapy with families. In my experience, the patterns she describes occur with any group of people when confronted by change.
I use this model to select how to help a group make a successful transformation from an Old Status Quo to a New Status Quo. Table 1 summarizes my suggestions on how to help during each stage of the change model:
| Stage | Description | How to Help |
| 1 | Late Status Quo | Encourage people to seek improvement information and concepts from outside the group. |
| 2 | Resistance | Help people to open up, become aware, and overcome the reaction to deny, avoid or blame. |
| 3 | Chaos | Help build a safe environment that enables people to focus on their feelings, acknowledge their fear, and use their support systems. Help management avoid any attempt to short circuit this stage with magical solutions. |
| 4 | Integration | Offer reassurance and help finding new methods for coping with difficulties. |
| 5 | New Status Quo | Help people feel safe so they can practice. |
| Table 1. Actions for each stage that will help a group change more quickly and effectively. |
The actions in Table 1 will help people cope. Actions that inhibit coping retards an organization’s ability to make core changes. These organization are resisting the fundamental foreign element of change. But organizations that create a safe environment where people are encouraged to cope increase their capacity for change and are much more able to respond effectively to whatever challenges are thrown their way.